Search results
Search for "chemical systems" in Full Text gives 19 result(s) in Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry.
Enabling artificial photosynthesis systems with molecular recycling: A review of photo- and electrochemical methods for regenerating organic sacrificial electron donors
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1198–1215, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.88
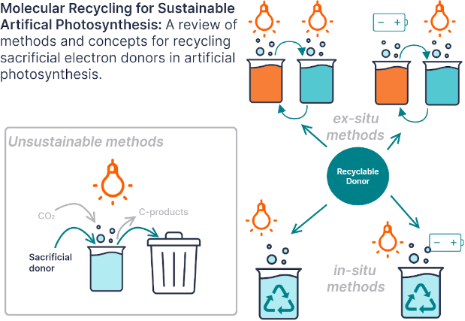
- discovery and creation of incredible chemical systems and materials. The ultimate goal is to harness energy from the sun and use it to transfer electrons and protons from water onto carbon dioxide and create molecules to replace fossil fuels [1][2]. However, when developing the components of artificial
- of simpler chemical systems with less components and less factors to optimize per reactor. This would require less re-optimization of existing chemistry. Recyclable donors could be stored in tanks like RFB electrolytes, which decouples the 2 reactions and means rates do not have to be perfectly
Polymer and small molecule mechanochemistry: closer than ever
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2022, 18, 1225–1235, doi:10.3762/bjoc.18.128

- sample, etc. All these effects superimpose and influence the intrinsic reactivity of the reagents [7]. At present, both mechanochemical approaches have proven highly versatile to activate numerous chemical systems and their applicability is expected to grow. Therefore, understanding the similarities and
- of each method to strain chemical systems on different length- and timescales, new studies have proven that the disparity is slowly becoming less pronounced. For example, with regards to the accepted higher directionality to induce mechanical deformation at the molecular level exhibited by
Scope of tetrazolo[1,5-a]quinoxalines in CuAAC reactions for the synthesis of triazoloquinoxalines, imidazoloquinoxalines, and rhenium complexes thereof
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2022, 18, 1088–1099, doi:10.3762/bjoc.18.111
- Laura Holzhauer Chloe Liagre Olaf Fuhr Nicole Jung Stefan Brase Institute of Biological and Chemical Systems, Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, Hermann-von-Helmholtz-Platz 1, 76344 Eggenstein-Leopoldshafen, Germany Institute of Nanotechnology, Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, Hermann-von
Effect of a twin-emitter design strategy on a previously reported thermally activated delayed fluorescence organic light-emitting diode
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2021, 17, 2894–2905, doi:10.3762/bjoc.17.197
- Augsburg, Universitätstrasse. 1, 86159 Augsburg, Germany Organic Semiconductor Centre, SUPA, School of Physics and Astronomy, University of St Andrews, North Haugh, St Andrews, KY16 9SS, UK Institute of Biological and Chemical Systems – Functional Molecular Systems (IBCS-FMS), Karlsruhe Institute of
Synthesis of new pyrazolo[1,2,3]triazines by cyclative cleavage of pyrazolyltriazenes
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2021, 17, 2773–2780, doi:10.3762/bjoc.17.187
- Nicolai Wippert Martin Nieger Claudine Herlan Nicole Jung Stefan Brase Institute of Biological and Chemical Systems – Functional Molecular Systems (IBCS-FMS), Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, Campus North, Hermann-von-Helmholtz-Platz 1, 76344 Eggenstein-Leopoldshafen, Germany Department of
Models of necessity
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 1649–1661, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.137
- , that are not contained in the quantum mechanical description of chemical systems, but has been used to derive machine-readable formats for storing and manipulating chemical structures in digital computers. This language is fuzzy and varies from chemist to chemist but has been astonishingly successful
- these models be extended to cover all relevant properties and characteristics of chemical systems. This, in turn, imposes conditions such as completeness, compactness, computational efficiency and non-redundancy on the extensions to the almost universal Lewis and VSEPR bonding models. Thus, AI and ML
Steric “attraction”: not by dispersion alone
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2018, 14, 1482–1490, doi:10.3762/bjoc.14.125

- of the other is greater than the electron–electron and nuclei–nuclei repulsion. The crucial role of charge penetration has been demonstrated for a diverse range of chemical systems, including the saturated [9][28] and unsaturated hydrocarbons [30], nucleic acids [31], metal ions interacting with
A recursive microfluidic platform to explore the emergence of chemical evolution
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2017, 13, 1702–1709, doi:10.3762/bjoc.13.164

- for chemical systems within an automated microfluidic platform that allows the creation of a population of individuals, the application of selection pressure, selection, combination, then splitting of the members of the population. We have produced each of the modules individually in our laboratory
- production of species of comparable complexity to those found exclusively in biology, as depicted in Figure 1. Droplet compartmentalisation In our previous work, we described the assembly of a custom-made 3D printed robotic platform that uses artificial evolution to select for desired behaviours in chemical
- systems [13]. In this case, the macroscopic behaviour of oil droplets was studied. We used a genetic algorithm to generate a series of droplets, each with a different set of chemical compositions, which were evaluated according to various fitness functions based on observable traits, such as motility
Chemical systems, chemical contiguity and the emergence of life
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2017, 13, 1551–1563, doi:10.3762/bjoc.13.155

- related to one aspect of cellular make-up, such as the formation of membranes or the build-up of information/catalytic apparatus. This approach is being gradually replaced by a more “systemic” approach that privileges processes inherent to complex chemical systems over specific isolated functional
- apparatuses. We will summarize the recent advances in system chemistry and show that chemical systems in the geochemical context imply a form of chemical contiguity in the syntheses of the various molecules that precede modern biomolecules. Keywords: chemical contiguity; chemical systems; geochemical
- these experiments. This short, necessarily selective, overview clearly underscores the necessity of new approaches, a fact that has led many researchers to propose the concept of chemical systems [22][23]. That is, the origin(s) of life, which is(are) hallmarked by the appearances of emergent properties
Grip on complexity in chemical reaction networks
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2017, 13, 1486–1497, doi:10.3762/bjoc.13.147

- oxidation of malonic acid (MA) [68][69]. Translation from the reaction scheme or equations (back) to the network motif, however, is far from intuitive. Hence, despite its beauty and obvious potential for making exciting discoveries, the BZ reaction (and similar classical chemical systems [70][71][72][73
Framing major prebiotic transitions as stages of protocell development: three challenges for origins-of-life research
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2017, 13, 1388–1395, doi:10.3762/bjoc.13.135

- current gap between chemistry and biology is still overwhelming, but also because the devil hides in the details. Prebiotic transitions are particularly tricky due to the fact that the chemical systems involved must work against the natural tendency towards thermodynamic equilibrium (i.e., they must find
- by COST Actions CM1304 (‘Emergence and evolution of complex chemical systems’) and TD1308 (‘Origins and evolution of life on Earth and in the Universe’).
Towards open-ended evolution in self-replicating molecular systems
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2017, 13, 1189–1203, doi:10.3762/bjoc.13.118

- described by Darwin in his famous work On the Origin of Species, but are still not understood in full detail [2]. It was only in the 1960’s that Spiegelman extended the scope of Darwinian evolution to chemical systems by studying the evolution of RNA-complexes [3]. In these experiments RNA was replicated
- Figure 1 [4]. These concepts can, in principle, be extended to what we will consider as Darwinian evolution in chemical systems. First the parent molecule, or replicator, is replicated to yield a large number of copies. This can for instance be achieved via an autocatalytic cycle, as will be discussed
- . Until now, chemical systems that show evolutionary behavior have involved relatively simple replicators that only had access to a very limited structural space of possible mutations. This rapidly causes the system to be incapable of exploring new structures and the development of novelty will stagnate
How and why kinetics, thermodynamics, and chemistry induce the logic of biological evolution
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2017, 13, 665–674, doi:10.3762/bjoc.13.66

- rule. Even though the Second Law remains an inescapable constraint, under energy-fuelled, far-from-equilibrium conditions, populations of chemical systems capable of exponential growth can manifest another kind of stability, dynamic kinetic stability (DKS). It is this stability kind based on time
- defined, that under appropriate contingent conditions, leads from chemistry to biology such that these two worlds merge into one. So, though life is a complex chemical system exhibiting complex kinetic behaviour, that complex behaviour can be traced back to self-reproducing chemical systems maintained far
- from equilibrium and directed by kinetic driving forces. Chemical systems able to evolve in the direction of increased dynamic kinetic stability – toward life – need to be endowed with three essential properties. They must be able to reproduce themselves, their structure should be compatible with the
Spectral and DFT studies of anion bound organic receptors: Time dependent studies and logic gate applications
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2017, 13, 222–238, doi:10.3762/bjoc.13.25

- progress ever since the first AND logic gate was mimicked with optical signals by de Silva and co-workers [31]. Myriads of chemical systems have been used by researchers towards the development of different functions such as AND, OR, NOT and their integrated operations [32]. Moreover the receptors with a
3D printed fluidics with embedded analytic functionality for automated reaction optimisation
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2017, 13, 111–119, doi:10.3762/bjoc.13.14
- of using 3D printing to produce microfluidic devices using AM techniques such as stereolithography (SL) [11], polymer jetting and fused deposition modelling (FDM) [12][13]. There is therefore considerable interest in the optimisation of chemical systems using this type of multifunctional continuous
Plakilactones G and H from a marine sponge. Stereochemical determination of highly flexible systems by quantitative NMR-derived interproton distances combined with quantum mechanical calculations of 13C chemical shifts
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2013, 9, 2940–2949, doi:10.3762/bjoc.9.331

- approach to investigate multiconformational chemical systems. Moreover, for the first time, we simultaneously assigned the relative configuration of four stereocenters by using the NOE analysis. In particular, the C-4 stereocenter is not adjacent to the other stereogenic carbons, highlighting that the NOE
Synthesis of nucleotide–amino acid conjugates designed for photo-CIDNP experiments by a phosphotriester approach
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2013, 9, 2898–2909, doi:10.3762/bjoc.9.326
- -lived DNA radicals, with a very high reaction rate by endogenous natural and synthetic compounds, which were extensively studied in chemical systems [1]. This “chemical way” of the DNA repair efficiently competes with the formation of modified sites, which are targets for the enzymatic repair. Since DNA
Structure elucidation of β-cyclodextrin–xylazine complex by a combination of quantitative 1H–1H ROESY and molecular dynamics studies
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2013, 9, 1917–1924, doi:10.3762/bjoc.9.226
- ; Introduction The emergence and establishment of supramolecular chemistry as an important domain of science has fueled the development of complex chemical systems from components, interacting by non-covalent intermolecular forces. This field transcends the traditional barriers separating many disciplines of
Liquid-crystalline nanoparticles: Hybrid design and mesophase structures
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2012, 8, 349–370, doi:10.3762/bjoc.8.39

- chemical systems [83] and is known as "re-entrance" [84]. The dendronised nanoparticles spontaneously self-assembled into a hexagonal lattice on the TEM grid: The mean distances between first and second neighbours were about 7.6 and 13.7 nm, respectively, in very good agreement with the NP diameter and the

























































































































































































![[Graphic 5]](/bjoc/content/inline/1860-5397-8-39-i5.png?max-width=637&scale=1.18182) phase of Au@C12/13 recorded with the beam (a) parallel to the
phase of Au@C12/13 recorded with the beam (a) parallel to the ![[Graphic 6]](/bjoc/content/inline/1860-5397-8-39-i6.png?max-width=637&scale=1.18182) pla...
pla...





![[Graphic 8]](/bjoc/content/inline/1860-5397-8-39-i8.png?max-width=637&scale=1.18182) symmetry composed of truncated octahedrons. Top right:...
symmetry composed of truncated octahedrons. Top right:...








